OctoLend Whitepaper
What, Why and how OctoLend
Introduction
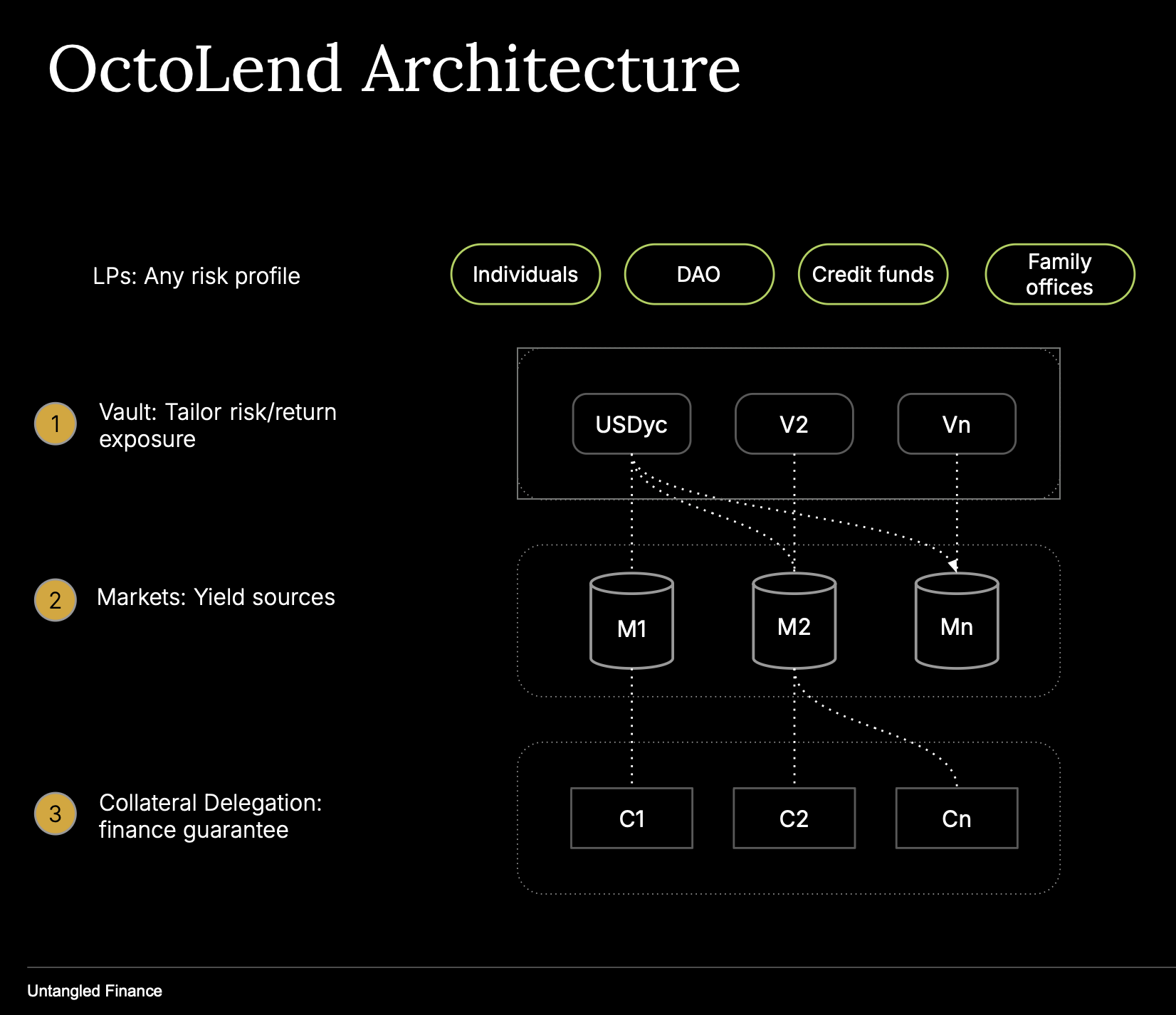
OctoLend is a curated lending protocol on Stellar Soroban composed of three modular pieces:
- Earn Vault (Vault V1): a permissionless, non-custodial vault that aggregates yield from Stellar protocols and issues a composable SAC share token.
- Lending Market: isolated, single-asset lending pools where LPs supply liquidity, borrowers post collateral (including delegated collateral), and interest, repayment, and liquidation are handled fully on-chain. Each Lending Market is itself a Soroban vault issuing LP shares.
- Interest Rate Model (IRM): a utilization-aware controller bound to each market that prices debt, compounds interest, and exposes a transparent debt price used for accounting and liquidations.
Together, these components let curators launch yield products, enable borrowers to access predictable credit, and give depositors a simple path to on-chain returns—without centralized custody.
Why OctoLend?
Vault-Based Architecture → Modular & Composable
OctoLend is built around programmable vaults — the Earn Vault and the Market Vault. This modular architecture enables curators to optimize risk and return for liquidity providers by allocating across different lending markets, while the Earn Vault remains fully composable with the broader Stellar DeFi ecosystem. The result is a flexible and transparent framework that supports diverse yield strategies and institutional integration.
Isolated Lending Markets → Better Risk Management
Each OctoLend Market is a self-contained lending pool pairing one collateral asset with one loan asset. Markets are isolated, meaning risks remain contained within each pool. Certain core parameters (such as the interest rate model configuration and liquidation parameters) are set once at initialization, while a limited set of operational parameters (e.g. oracle, fee settings, pause state) can be updated by an authorized admin under defined on-chain rules. This ensures predictable behavior, limits systemic contagion, and gives lenders and borrowers clear, quantifiable exposure.
Configurable Interest Rate Model → Higher Capital Efficiency
Each Market binds to a configurable Interest Rate Model (IRM) whose parameters are set once at market initialization. The IRM adapts borrowing rates to utilization in real time, tightens spreads under normal conditions, and escalates rates predictably under stress using an internal “stress memory.” The outcome is greater capital efficiency, enabling higher borrowing capacity without compromising liquidity safety.
Collateral Delegation → Decentralized Underwriting
A dedicated Collateral Vault allows curators to delegate first-loss collateral to trusted borrowers under predefined on-chain policies (e.g., minimum collateral, allocation caps, and delegation fees). This separates capital provision from credit selection, decentralizing underwriting while unlocking new use cases for institutional and RWA-backed lending.
Reward Layer → Incentivized Participation
OctoLend can support additional reward layers (e.g., OCTO, stablecoins, or other fungible assets) as an optional higher-level module. Reward accounting may occur off-chain for efficiency, with on-chain distribution and claims executed via a Merkle-based contract, ensuring transparent and verifiable reward delivery.
Earn Vault (Vault V1)
What it is
A Vault holds one base asset (e.g., USDC) and issues a share token representing proportional ownership of total value. Curators deploy and manage vaults via the Untangled Curator App, allocating capital across Stellar protocols such as OctoLend markets. Users deposit once for diversified exposure and redeem via epoch-based (asynchronous) withdrawals. Vaults are immutable and controlled by multisig or MPC infrastructure (e.g., LOBSTR Vault, Fireblocks).
Key properties
- Soroban-based standard: open, audited contracts.
- Composable shares: SAC tokens compatible with wallets and DeFi protocols.
- Non-custodial treasury: curator-controlled; Untangled does not custody funds.
- Flexible strategy: combine DeFi and RWA yields.
- Async withdrawals: deposits are instant; redemptions are processed per epoch.
- Transparency: NAV, allocations, and share price are on-chain; valuation logic is curator-run off-chain.
How it works
- Curation & strategy: curator selects protocols and allocates via the treasury wallet.
- Valuation: distributor updates share price from off-chain NAV (reflecting earnings and fees).
- User flows: users mint shares on deposit; submit withdrawal requests and are settled post-epoch.
Roles
- Issuer: deploys SAC share token and defines permissions.
- Distributor: updates share price and processes redemptions.
- Curator/Treasury: executes strategy, settles epochs, and manages allocations.
At a glance
- Permissionless deployment.
- Non-custodial and immutable.
- Composable SAC shares.
- Audited and open source (Veridise).
Markets (Lending)
What it is
A Lending Market is a single-asset credit engine implemented as a Soroban vault. LPs deposit the underlying asset and receive market shares. Borrowers post collateral directly to the market and may augment it with delegated collateral from a Collateral Vault. Borrower debt is tracked internally as debt shares, whose value is determined by the market’s IRM-derived debt price.
Each market is self-contained: its asset, collateral, oracle, IRM configuration, and liquidation parameters are bound to that instance.
Purpose
- Isolated lending pools with predictable, local risk.
- Support both posted collateral and delegated collateral.
- Deterministic debt pricing via the market’s IRM.
Core components
- Underlying asset (supply side): LPs deposit this asset; borrowers receive it on borrow.
- Debt shares: internal accounting unit tracking borrower debt, priced via the IRM debt price (7 decimals).
- Oracle (SEP-40 style): provides price and decimals for the collateral asset; used for LTV and liquidation checks.
- Liquidation LTV (LLTV): threshold (in basis points) at which a position becomes liquidatable.
- Interest Rate Model: computes utilization, borrow rates, compounding, and debt price.
- Market treasury: the market contract itself holds underlying liquidity; borrows and repayments move assets to and from the contract balance.
- Collateral Vault (optional): delegates collateral to named borrowers, increasing effective collateral.
User flows
- Supply / Withdraw (LPs): LPs interact via standard vault actions (
deposit,mint,withdraw,redeem). Interest is compounded and fees are accrued before these actions execute; withdrawals are subject to available on-chain liquidity. - Borrow / Repay: borrowing capacity is determined by the value of posted collateral plus delegated collateral versus LLTV. Borrows transfer underlying assets from the market contract to the borrower. Repayments return assets to the market contract and burn debt shares. Both borrow and repay operations first compound interest and accrue fees. Partial repayment is supported, and overpayment is capped to the exact amount required to fully repay outstanding debt shares.
Access control
- Admin: may pause or unpause the market, configure fees and fee beneficiary, toggle delegation support, set the collateral vault, and manage oracle updates (subject to timelock).
- Pause state: when paused, all state-changing actions (borrowing, repaying, collateral actions, liquidations, and vault deposits/withdrawals) are blocked; read-only queries remain available.
Oracle governance
- Initial setup: the oracle is set immediately if none exists.
- Updates: subsequent oracle changes are subject to a mandatory 48-hour on-chain timelock. An admin proposes a new oracle, which becomes executable only after the timelock elapses. Pending updates may be queried or cancelled before execution.
Interest Rate Model (IRM)
What it is
A utilization-aware controller that (i) returns an annualized borrow rate, (ii) compounds total debt assets over time, and (iii) provides a debt price (value per debt share) used across accounting and liquidations. The model stabilizes around an optimal utilization and escalates above a critical utilization with a time-dependent stress component, while damping rates at low utilization.
Goals
- Keep markets liquid and predictable.
- Encourage repayments or fresh supply at high utilization.
- Avoid punitive rates when usage is low.
- React quickly during stress, then decay back toward equilibrium.
What it controls
- Current annualized borrow rate (derived from per-second dynamics).
- Compounded growth of total debt assets between accruals.
- Debt price for valuing borrower debt positions.
Key parameters (set once per market)
- u_opt, u_crit, u_low — utilization targets and bounds.
- k_lin, k_i, k_crit, k_low — slopes and gains controlling baseline, integral, penalty, and low-utilization damping behavior.
- beta — stress memory adaptation speed.
- r_i, t_crit — internal IRM state variables.
Lifecycle
- Bound to a market at deployment; configuration can only be set once.
- Accrual updates internal state, advances timestamps, and compounds total debt assets.
- Exposes current rate and debt price for real-time monitoring and liquidation logic.
Liquidations
A position is liquidatable when:
borrowed_value > collateral_value × (LLTV / 10_000)
where:
borrowed_value = debt_shares × debt_price
collateral_value = (posted_collateral + delegated_collateral) × oracle_price
Delegation fees accrue off-balance-sheet and are not netted out of delegated collateral when calculating collateral value, borrow capacity, liquidation thresholds, or vault share prices; they are settled separately when paid or forfeited.
Flow
- The protocol determines whether liquidation is allowed; if allowed, the entire borrowed value is available to liquidate.
- The liquidator specifies either the number of debt shares to repay or the amount of collateral to seize; the protocol computes the other side deterministically.
- The liquidator repays underlying assets to the market and receives collateral worth the repaid value multiplied by
(1 + bonus_bps / 10_000)at the oracle price. - Seizure order: the borrower’s posted collateral is seized first. If insufficient, the remaining shortfall is recorded as a pending seize against delegated collateral.
- If delegated collateral is implicated, the market emits a pending-seize record that the Collateral Vault later settles via
liquidate_allocation. - Partial liquidation is supported, enabling gradual deleveraging and reduced market impact.
Collateral Delegation
Overview
The Collateral Vault supplies a programmable credit-enhancement layer. Curators pool collateral, delegate it to trusted borrowers, and borrowers allocate portions of that delegation to specific lending markets—without rehypothecating assets.
Three accounting layers
- Deposits: vault assets → vault shares.
- Delegations: borrower-specific delegated balances.
- Allocations: portions of delegated balances actively allocated to a given market.
Receiver policy (per borrower)
- max_allocation_rate: cap on allocation relative to borrower’s posted collateral in the linked market.
- min_collateral: minimum posted collateral required before delegation can be allocated.
- delegation_fee_bps: annualized fee on allocated amounts; accrues linearly over time.
Capacity & safety
- Remaining capacity = vault asset balance − total delegated.
- Withdrawals and redemptions are immediate but constrained so that delegated collateral remains fully covered.
- No rehypothecation; strict custody and on-chain auditability.
Additional rules
- Receiver configuration cannot be changed once a borrower has active delegated collateral.
- Delegation fees accrue over time and may be paid explicitly by the borrower or forfeited upon liquidation.
Fees
Types
- Borrow interest (IRM): interest accrues continuously on debt and is compounded into total debt assets, increasing the debt price over time.
- Delegation fee (Collateral Vault): borrower-specific fee on allocated delegated collateral; accrues linearly and is tracked on-chain. Unpaid fees may be forfeited on default.
- Market fee (Lending Market): a configurable portion of interest growth minted as additional market shares to a designated fee beneficiary.
- Liquidation bonus: not a protocol fee, but a parameterized incentive paid in extra collateral to liquidators.
Transparency
On-chain getters expose utilization, debt price, total debt assets, accrued fees, and fee parameters, enabling real-time monitoring and independent verification.
Immutability
Markets and vaults are isolated from one another. Certain parameters (such as IRM configuration and liquidation thresholds) are set once at initialization, while others (such as fee rates, fee beneficiary, oracle, and pause state) may be updated by an authorized admin under explicit on-chain rules.
Rewards
OctoLend may support additional reward streams (e.g., OCTO, stablecoins, or other fungible tokens) as an optional layer above the core protocol. Reward accounting can be performed off-chain, with on-chain distribution and claims handled via Merkle-based contracts on Stellar.