Collateral Delegation
Decentralize credit underwriting
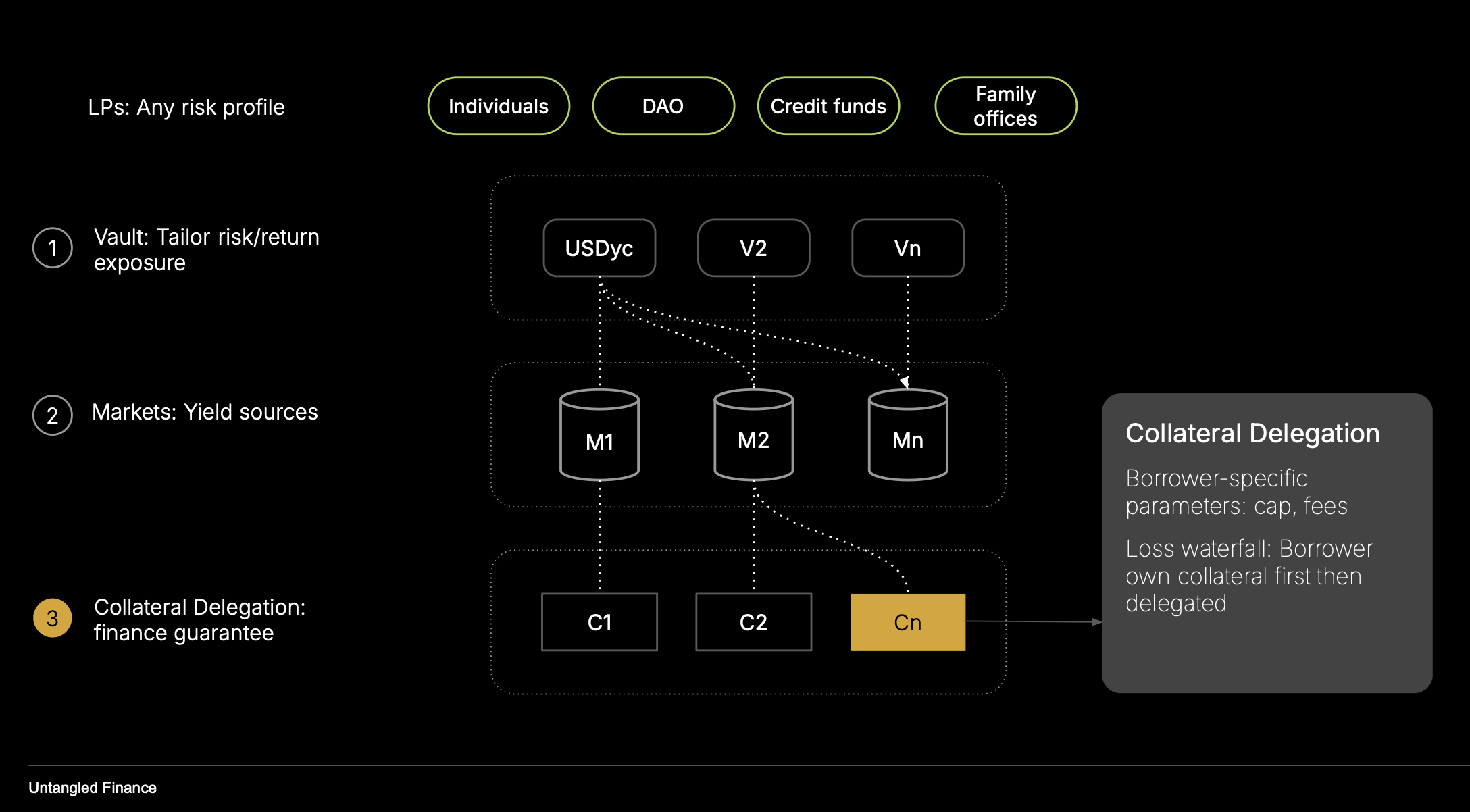
Overview
The Collateral Vault is the additional underwriting layer of OctoLend. It provides programmable credit enhancement by allowing collateral assets to be pooled on-chain and delegated to trusted borrowers or credit facilities.
Delegated collateral may then be allocated into specific lending markets, increasing a borrower’s effective collateral without rehypothecating assets or transferring custody.
The Collateral Vault holds assets on-chain at all times and enforces delegation and allocation rules through deterministic smart contract logic.
Purpose
As in traditional lending protocols, borrowers may post their own collateral to borrow. In addition, collateral can be pooled by institutional providers and delegated to borrowers under controlled on-chain policies, enabling:
- Bootstrapping of real-world assets (RWAs) whose on-chain liquidity is still developing.
- Decentralized underwriting with explicit first-loss participation.
- Configurable credit support that mirrors off-chain credit facilities while remaining transparent and non-custodial.
Core Mechanism
The vault manages three layers of accounting:
| Layer | Description | Stored As |
|---|---|---|
| Free | Assets supplied by depositors and not currently delegated. Issued as vault shares. | Vault::total_assets() |
| Delegated | Collateral amounts delegated to receivers (potential borrowers). | Delegation(Address) |
| Allocated | Portions of delegated collateral actively committed to a borrower in a specific lending market. | Allocation(Address, market) |
Delegations determine who may borrow, while allocations determine how much delegated collateral is currently in use. Both are strictly constrained by the vault’s on-chain asset balance.
Receiver Policies
Each receiver (borrower or credit facility) operates under a configurable policy that governs how delegated collateral may be used:
- max_allocation_rate: Maximum ratio between allocated delegation and the borrower’s posted collateral in the linked lending market.
- min_collateral: Minimum amount of borrower-posted collateral required before delegation can be activated.
- delegation_fee_bps: Annualized fee rate charged on allocated amounts, accruing linearly over time.
These parameters ensure delegated credit remains capital-efficient while enforcing conservative risk bounds. Receiver configuration is locked once a borrower has an active delegated balance.
Delegation and Allocation Flow
1. Deposit
- Users deposit collateral assets (e.g., XLM or tokenized RWAs) into the Collateral Vault and receive vault shares.
- Assets remain held directly by the vault contract and are never transferred out during delegation.
2. Delegation
- A curator delegates a portion of the vault’s available collateral to a borrower (receiver).
- The vault checks remaining capacity using:
Delegation does not move assets; it only records a credit limit for the receiver.
3. Allocation to Credit
- When a borrower draws credit from a linked lending market:
- A portion of their delegated collateral is allocated to that market.
- Policy limits (
min_collateralandmax_allocation_rate) are enforced. - Delegation fees begin accruing based on
delegation_fee_bpsand time elapsed.
Allocation represents collateral actively backing a market position but does not transfer custody of assets.
4. Deallocation / Liquidation
- As the borrower repays or unwinds their position, allocations are reduced or fully deallocated.
- Released delegated capacity becomes available again for new allocations or borrowers.
- In the event of liquidation, allocated collateral may be seized by the lending market via a pending-seize mechanism and later reconciled by the vault.
Fee Accrual
Delegation fees accrue linearly over time according to:
Fees are tracked per allocation and aggregated at the vault level. Accrued fees are an accounting entry and do not reduce delegated collateral or vault share value until explicitly paid or forfeited.
Integration with Lending Markets
Delegation is borrower-specific and market-agnostic:
- Each Lending Market may reference at most one Collateral Vault.
- A single Collateral Vault may delegate collateral to many borrowers across multiple markets.
When collateral is allocated or deallocated:
- Allocation limits are enforced internally by the vault.
- Lending markets may only rely on delegated collateral up to the currently allocated amount.
This preserves composability while maintaining strict custody and risk isolation.
Risk Controls
The Collateral Vault enforces multiple layers of safety:
- Isolation: Each vault is self-contained; failures do not propagate across markets.
- Policy enforcement: Borrowers cannot exceed configured allocation limits or bypass
min_collateralrequirements. - No rehypothecation: Assets remain escrowed within the vault contract at all times.
- Fee transparency: All fees, delegations, and allocations are tracked on-chain and auditable in real time.
- Liquidity protection: Withdrawals and redemptions are constrained so that delegated collateral remains fully covered.
Example Use Case
An RWA issuer wants to bootstrap liquidity for a new tokenized treasury fund:
- Institutional providers deposit XLM into a Collateral Vault.
- The RWA issuer receives a delegation capped at 50% of their posted on-chain collateral.
- The issuer allocates part of that delegation to open a credit line in a linked OctoLend lending market.
- Delegation fees accrue to providers, compensating them for taking first-loss exposure.
- When the loan is repaid, allocations are released and delegation capacity resets.
Summary
The Collateral Vault transforms pooled collateral into a programmable, on-chain credit enhancement layer.
It enables curators and institutions to distribute credit capacity transparently and securely, while maintaining strict isolation, non-custodial guarantees, and capital efficiency.
By decoupling collateral provision from borrowing, OctoLend enables on-chain credit markets that more closely resemble real-world credit facilities—while remaining permissionless, auditable, and composable.