Market
Compose yield strategy
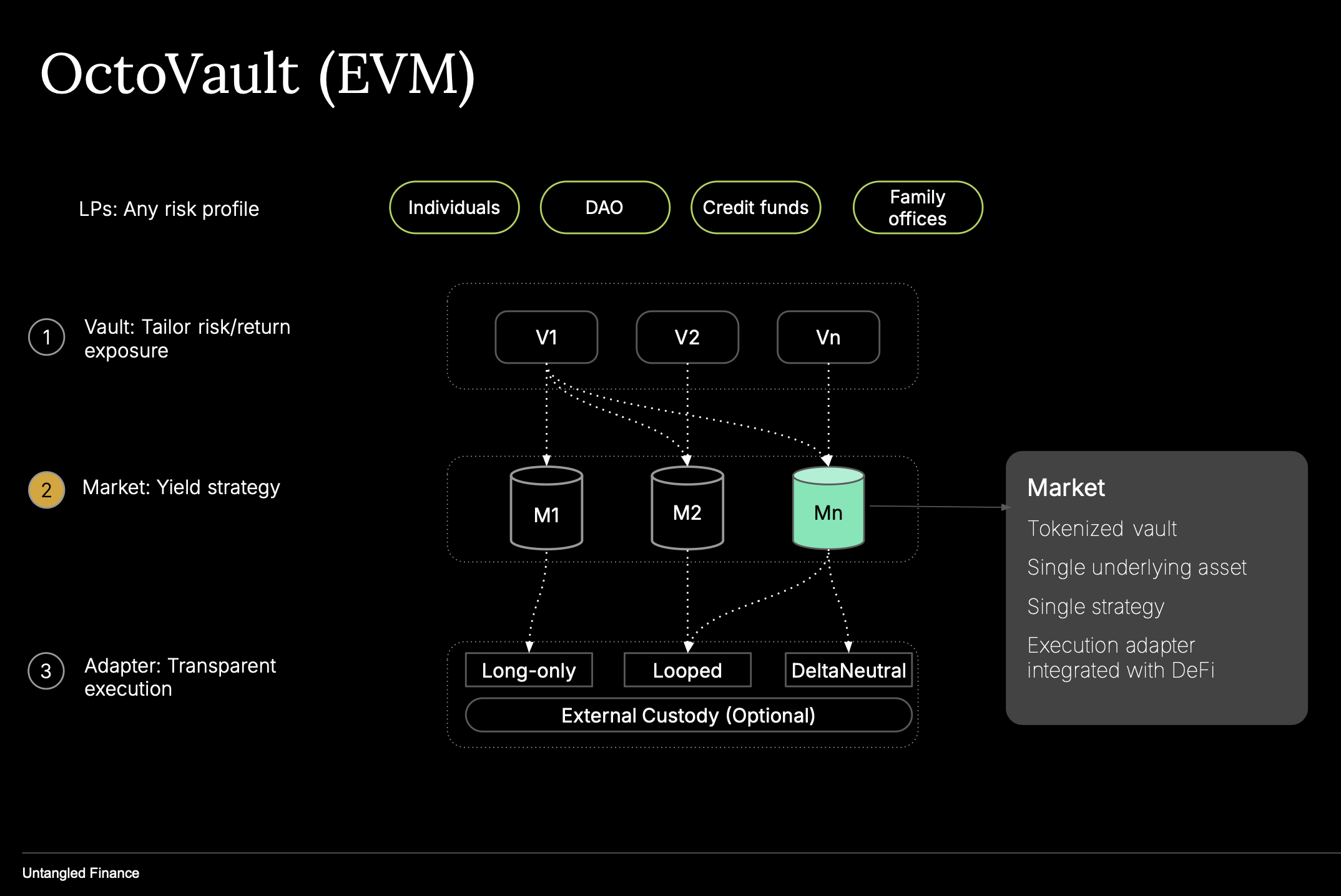
Overview
A Market in OctoVault is an ERC-4626 vault extended from the BasedVault base class.
It encapsulates three fundamental components:
- An Asset: the ERC-20 token the Market accepts and accounts for, such as USDC, stETH, or RWA tokens.
- A Strategy: the logic defining how deposited assets are deployed, borrowed, or hedged.
- An Execution Path: a sequence of venues, adapters, and transactions that implement that strategy.
Each Market represents a single-strategy, isolated vault that can be combined with others through a parent Vault (MetaVault).
It is the operational layer of OctoVault where strategy execution takes place across DeFi protocols.
Strategies
OctoVault defines Markets by strategy type, not by configuration parameters.
Different Market contracts implement different strategy behaviours, allowing composable structured yield products.
Looped Market
A Looped Market borrows against its deposits to create leveraged exposure or yield amplification.
Flow
- The Market receives ERC-20 supply from a Vault.
- It acts as a borrower in an isolated lending market via an Adapter, such as Silo, Morpho, or Euler.
- The borrowed funds are looped back into the same or another ERC-20 asset to compound yield or basis spread.
Example
Supply USDC → Borrow USDT → Swap to USDC → Re-supply to the lending market.
The position amplifies base lending APY, offset by borrow costs.
Accounting
- Assets = Supplied + Re-supplied positions
- Liabilities = Outstanding borrow balance
- Net Asset Value (NAV) = Assets − Liabilities, reflected in the Market share price
Use cases Levered RWA vaults, levered liquid staking, or leveraged stablecoin carry trades.
Hedged LP Market
A Hedged LP Market provides liquidity to a perpetual DEX while neutralising market risk through on-chain hedging.
Flow
- The Market receives ERC-20 assets from a Vault, such as USDC or ETH.
- It swaps them for LP tokens of a Perp DEX, such as GMX, Hyperliquid, or Ostium.
- It opens short perpetual positions equal to the LP’s underlying exposure.
Result A delta-neutral position that earns funding and fee yield with minimal directional risk.
Accounting
- Assets = LP token positions + collateral balances
- Liabilities = Short perp notional exposure
- NAV = Net mark-to-market value across both legs
Use cases Delta-neutral vaults, funding-rate arbitrage, or market-neutral liquidity provisioning.
Execution Path
Each Market contains an execution path that defines:
- The underlying venues used, such as lending markets, DEXs, or perpetual venues
- The Adapters that interface with those venues
- The sequence of steps in execution order, such as supply → borrow → swap → stake
Execution is performed through the following functions:
- Market.supply(adapter, data)
- Market.withdraw(adapter, data)
- Market.harvest(adapter, data)
- Market.multicall(adapter, data[])
These methods allow the curator or its automation engine to control all operational aspects of the Market — from opening positions to harvesting rewards — through a single on-chain interface.
Each Adapter implements IAdapter, defining how a specific venue behaves, ensuring predictable and secure integration across protocols.
Risk Parameters
Every Market operates under a defined risk policy.
Key parameters include:
- Size or borrow limits (LTV%)
- Maximum leverage ratio
- Utilisation thresholds
- Whitelisted venues and token pairs
These parameters define how aggressive or conservative a Market’s strategy can be.
They are configured and adjusted by the Market Curator either:
- Manually through governance, or
- Automatically via an off-chain risk engine or AI agent that monitors market conditions and adjusts parameters programmatically.
Multi-Venue and Rebalancing
Each Market can have multiple underlying venues of each type:
- Multiple lending markets for diversification, such as Euler and Morpho
- Multiple DEXs or perpetual venues for hedging, such as GMX and Hyperliquid
This enables venue rotation based on yield, funding, or liquidity depth. Rebalancing between venues optimises returns or reduces risk.
Rebalancing is triggered by the curator or an external optimisation engine that analyses on-chain and off-chain metrics and proposes new allocation weights through standard timelocked actions.
Market Structure and Accounting
- Each Market’s accounting mirrors the Vault model but focuses on its strategy composition.
- Market share value increases as net portfolio value rises, calculated as assets minus liabilities.
- Value accrues automatically to the ERC-4626 share price, meaning depositors see returns via increasing share-to-asset ratios.
- Short positions or borrowed assets are explicitly represented as negative balances in NAV calculations.
- A Market can supply another Market if its execution path defines that dependency, enabling nested strategy composition.
This modular accounting model enables multi-layered strategies, such as Vault → Looped Market → Hedged Market → RWA pool.
Customisation
Developers can extend Market behaviour by:
- Implementing new Adapters to support novel venues or RWA protocols
- Overriding internal valuation logic for synthetic or off-chain assets
- Adding risk modules that dynamically adjust LTV or leverage limits
If a Market is repurposed for a non-standard use case such as synthetic delta hedging or off-chain credit, its share accounting logic can be overridden to reflect the new valuation model.
Summary
The Market is the strategy execution engine of OctoVault.
- It turns ERC-20 capital into active, risk-isolated strategies.
- It represents a single, composable building block of structured yield.
- It can loop, hedge, lend, or combine these paths transparently under ERC-4626.
- It accrues value to its shares based on portfolio NAV, including both long and short exposures.
- It allows automated or curator-driven optimisation with complete risk and custody control.